Abstract
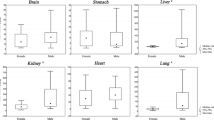
In order to elucidate the distribution of elements in organs from healthy Japanese, instrumental neutron activation analysis (INAA), based on the preliminary examination, was applied to quantitative determination of multielements in nine organs autopsied (brain, heart, kidney, liver, lung, muscle, pancreas, spleen, and thyroid). The following results were obtained: (1) The values obtained for each element could be considered to be representative as "normal values" and "ranges" in organs from healthy Japanese males; (2) the essential elements Br, Cl, Co, Cu, Fe, K, Mn, Na, Rb, Se, and Zn were not affected by external environmental factors or by racial difference; (3) renal and hepatic Cd levels were very high in several cases and the accumulation has still been in progress in the Japanese, whereas the contaminant elements are low in each organ except for lung.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. S. Snyder, M. J. Cook, E. S. Nasset, L. R. Karhausen, G. P. Howells, and I. H. Tinpton, Report of the Task Group on Reference Man. International Commission on Radiological Protection No. 23, Pergaman Press, Oxford (1974).
E. J. Underwood, Trace Elements in Human and Animal Nutrition, Academic, New York (1977).
G. V. Iyengar, W. E. Kollmer, and H. J. M. Bowen, The Elemental Composition of Human Tissues and Body Fluids, Verlag Chemie, Weinheim (1978).
T. G. Aalbers, Cardiovascular diseases and trace elements, Durukkerij Blok en Zonen, Dieren, private communication.
S. Takacs and A. Tatar, Trace elements in the environment and in human organs: analysis according to domicile and sex. Z. Gesamte Hyg. 37, 53–55 (1991).
E. Andrasi, M. Suhajda, I. Saray, L. Bezur, L. Ernyei, and A. Reffy, Concentration of elements in human brain: glioblastoma multiforme, Sci. Total Environ. 139/140, 399–402 (1993).
R. Zeisler, P. Ostapczuk, S. F. Stone, and M. Stoeppler, Effective tools for the trace element characterization of tissues: neutron activation analysis and voltammetry, Sci. Total Environ. 139/140, 403–410 (1993).
T. Takeuchi, Y. Nakano, A. Aoki, S. Ohmori, and T. Tsukatani, Comparisons of elemental concentrations in hair of the inhabitants of heavy metal polluted areas with those of normal Japanese, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 112, 259–272 (1987).
T. P. Cheng, J. S. Morris, S. R. Koirtyohann, V. L. Spate, and C. K. Baskett, Study of the correlation of trace elements in carpenters’ toenails, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 195, 31–42 (1995).
F. A. EI-Amri and M. A. R. EI-Kabroum, Trace element concentrations in human bone using instrumental neutron activation analysis. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 217, 205–207 (1997).
G. Ingrao, P. Belloni, S. D. Pietro, and G. P. Santaroni, Levels of some trace elements in selected autopsy organs, and in hair and blood samples from adult subjects of Italian population, Biol. Trace Element Res. 26–27, 699–708 (1990).
J. Bacso, D. Balazs, I. Uzonyi, G. Lusztig, and I. Szigety, Study of relationships between micro element contents of human hair and other tissues in connection with environmental contamination and some diseases, Report on an IAEA Co-ordinated Research Programme, NAHRES-18, pp. 5–26 (1993).
Y. D. Cheng, G. S. Zhuang, and Y. X. Zhaung, Study on correlation of trace elements in human hair and internal organs by nuclear methods, Report on an IAEA Co-ordinated Research Programme, NAHRES-18, pp. 27–50 (1993).
J. Matsubara, T. Sato, and S. Ohomori, Correlation among multi-elemental concentrations in liver, kidney and hair of humans, Report on an IAEA Co-ordinated Research Programme, NAHRES-18, pp. 87–99 (1993).
E. Sabbioni, C. Minoia, R. Pielna, S. Fortaner, M. Gallorini, and A. Saltelli, Trace element reference values in tissues from inhabitants of the European community, Sci. Total Environ. Res. 120, 39–62 (1992).
J. Yoshinaga, H. Imai, M. Nakazawa, T. Suzuki, and M. Morita, Lack of significantly positive correlations between elemental concentrations in hair and in organs, Sci. Total Environ. 99, 125–135 (1990).
Y. Yamamoto, T. Sato, K. Mori, et al., Concentrations of trace elements in the hair, liver and kidney from autopsy subjects by neutron activation analysis, Res. Pract. Forensic Med. 34, 97–108 (1991).
Y. Katoh, T. Sato, and Y. Yamamoto, Multielemental analysis for human organs, Bull. Tokyo Metropol. Coll. Allied Med. Sci. 8, 177–185 (1995).
K. Sumino, K. Hayakawa, T. Shibata, and S. Kitamura, Heavy metals in normal Japanese tissues, Arch. Environ. Health 30, 487–494 (1975).
M. Yukawa, M. Suzuki-Yasumoto, K. Amano, and M. Terai, Distribution of trace elements in the human body determined by neutron activation analysis, Arch. Environ. Health 35, 36–44 (1980).
H. Teraoka, Distribution of 24 elements in the internal organs of normal males and the metallic workers in Japan, Arch. Environ. Health 36, 155–164 (1981).
K. Nishiyama, T. Miki, S. Sakurai, et al., Distribution of trace elements in normal human organs and tissues determined by neutron activation analysis. Co-operative Research (A) 5730014 supported by Grand in Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Study Report (1985).
Y. Katoh, T. Sato, and Y. Yamamoto, A preliminary study on determination of concentrations of multi-element in human organs using INAA, in press.
T. Sato, Activation analysis of biological materials, in Activation Analysis, Z. B. Alfassi, ed., CRC, New York, Vol. II (1990).
N. I. Ward and J. A. Mason, Neutron activation analysis techniques for identifying elemental status in Alzheimer’s disease, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 113, 515–526 (1987).
J. D. Stedman and N. M. Spyrou, Elemental analysis of the frontal lobe of normal brain tissue and that affected by Alzheimer’s disease, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 217, 163–166 (1997).
T. G. Aalbers, J. P. W. Houtman, and B. Makkink, Trace-element concentrations in human autopsy tissue, Clin. Chem. 33(11), 2057–2064 (1987).
Y. Wang, G. Zhuang, M. Tan, M. Zhi, and Y. Cheng, Distribution of some elements in human hair and internal organs, determined by neutron activation analysis, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 151, 301–311 (1991).
L. Tandon, E. J. Kasarskis, and W. D. Ehmann, Elemental imbalance studies by INAA on extraneural tissues from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 195, 13–19 (1995).
W. J. Altaf and N. M. Spyrou, Evaluation of concentrations of major and trace elements in human lung using INAA and PIXE, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 217, 201–204 (1997).
S. O. Rogero, M. Saiki, P. H. N. Saldiva, and M. L. Daliberto, Determination of trace elements in human lung samples, Biol. Trace Element Res. 43–45, 489–496 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katoh, Y., Sato, T. & Yamamoto, Y. Determination of multielement concentrations in normal human organs from the Japanese. Biol Trace Elem Res 90, 57–70 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:90:1-3:57
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:90:1-3:57